-

The Role of Integrating Nutrition Counseling in Family Medicine Didactics on the Confidence Level of Family Medicine Residents to Provide Counseling to Their Patients
Saniya Jain, Kelsey Mellow, and Matthew Sebastian
Publication Date: 3-13-2025
Aim
- The purpose of the project is to study the role of integrating nutrition counseling in family medicine didactics on the confidence level of family medicine residents to provide counseling to their patients.
-
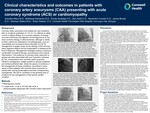
Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes in Patients with Coronary Artery Aneurysms (CAA) Presenting with Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) or Cardiomyopathy
Advaitha Misra, Mathangi Keshavan, Ersida Zerdelija, Zain Abidi, Alexandra Corrado, James Benke, Ghassan Dalloul, and Anton Salwan
Publication Date: 3-13-2025
Coronary artery aneurysms and ectasia are rare conditions with an incidence estimated at < 1% [1]. It is defined as either a focal or diffuse dilation of a coronary segment of at least one and a half times the adjacent normal segment [2,3].The most common etiology is atherosclerosis, although a variety of other culprits are implicated in its pathogenesis, such as vasculitidies and connective tissue disorders [3,4,5]. Its management is largely driven by the etiology of the coronary artery segment dilation and the presentation of disease at the time of diagnosis. Management strategies employ a judicious combination of medical therapy, percutaneous and surgical interventions. The presence of coronary artery aneurysm or ectasia has been associated with poor long-term outcomes [6,7,8]. Complications from coronary artery aneurysm influence management, largely guided by clinician judgment and limited published data. Given the paucity of evidence in the management of these conditions, we present a case series of three patients with coronary artery aneurysm or ectasia with varying presentations and their corresponding management. We aim to contribute to the growing body of evidence for the management of this elusive cardiac condition.
-

Mounjaro Mediated Drug-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia
Barbara Senger, Zachary Howarth, Ali Baydoun, and Benjamin Rossi
Publication Date: 3-13-2025
Introduction:
▪ Thrombocytopenia is a condition in which a person has low platelets or thrombocytes in the blood.
▪ Symptoms of thrombocytopenia vary based on severity.
▪ Mild: asymptomatic.
▪ Moderate: prolonged bleeding following trauma, easy ecchymosis, petechiae and purpura.
▪ Severe: spontaneous ecchymosis/petechiae/purpura, spontaneous mucosal bleeding, life threatening internal bleeding.
-

The Role of Integrating Nutrition Counseling in Family Medicine Didactics on the Confidence Level of Family Medicine Residents to Provide Counseling to Their Patients
Saniya Jain, Kelsey Mellow, and Matthew Sebastian
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
The purpose of the project is to study the role of integrating nutrition counseling in family medicine didactics on the confidence level of family medicine residents to provide counseling to their patients.
-

Improving Completion Rates of Screening Colonoscopies
Lauren Lumley, Jordan Meyer, and Annie Craib
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
To identify barriers to completion of screening colonoscopies and identify/implement solutions to increase completion rates.
-

Mounjaro Mediated Drug-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia
Barbara Senger, Zachary Howarth, Ali Baydoun, and Benjamin Rossi
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
Thrombocytopenia is a condition in which a person has low platelets or thrombocytes in the blood.
Symptoms of thrombocytopenia vary based on severity.
Mild: asymptomatic.
Moderate: prolonged bleeding following trauma, easy ecchymosis, petechiae and purpura.
Severe: spontaneous ecchymosis/petechiae/purpura, spontaneous mucosal bleeding, life threatening internal bleeding.
-

The use of a short and user-friendly questionnaire as a screening tool to identify potential gaps in nutrition knowledge of adolescent athletes
Roben Ohev Shalom, David Lick, and Virginia E. Uhley
Publication Date: 5-2024
Nutrition knowledge in adolescent athletes is rarely formally assessed by physicians. Current popular nutrition questionnaires include the CDC’s Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBSS) and the Nutrition for Sport Knowledge Questionnaire (NSKQ). These questionnaires are long and are not optimal to assess nutrition knowledge in adolescent athletes at their preparticipation examinations. A systematic review conducted by Tam et al, showed that questionnaires would benefit from interactive and attractive features including images. A novel nutrition questionnaire was adapted from the NSKQ that was user friendly, short in length, electronic and included images. We hypothesized that through collecting physicians feedback on the questionnaire will allow us to create an improved screening tool that can be incorporated into sport physical exams to help identify specific nutrition knowledge gaps and related misconceptions of healthy eating patterns in adolescent youth.
-

Identifying Burnout Progression Amongst Residents
Emmett Smith
Publication Date: 5-9-2024
As a family medicine resident progresses through training, transitional periods can worsen burnout, especially when moving from one year to the next. These transitions bring increased responsibility, patient volume, following up on results, meeting educational requirements, and preparing for board exams. Collecting data on burnout during these times is crucial for identifying needs and implementing targeted resources to promote physician longevity, growth, and wellness. Additionally, this data will strengthen the residency program and benefit future doctors.
-

Near-Surface Dose Correlates With Moist Desquamation and Unplanned Reconstructive Surgery in Patients With Implant-Based Reconstruction Receiving Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy
Patrick Thrasher, Ronald Levitin, Bryan S. Squires, Allison J. Hazy, Michael J. Maywood, Anthony P. Delise, Muayad F. Almahariq, Nayana Dekhne, Lauren Oliver, Peter Y. Chen, Kailee J. Walters, Diane Dudley, and Joshua T. Dilworth
Publication Date: 5-2024
Postmastectomy radiation therapy (PMRT) utilized as part of a breast cancer treatment regimen reduces the risk of disease recurrence in appropriately selected patients.1,2,3,4,5 However, PMRT increases risk of radiationrelated toxicities that can interfere with breast reconstruction post-mastectomy.6 Following mastectomy, implant-based reconstruction can increase patient satisfaction and quality of life7,8; complications induced by PMRT such as infection and tissue contracture, though, increase risk for implant loss and may ultimately require further surgeries for the patient.
PMRT is delivered based on treatment plans that are optimized to provide appropriate radiation dosages to tissues along the chest wall while simultaneously limiting exposure of surrounding sensitive structures. Subcutaneous lymphatic structures and residual glandular tissue are of major importance as they may harbor microscopic disease that can lead to recurrence.9 The skin and immediate surrounding tissue, therefore, is often exposed to higher doses of radiation to ensure appropriate therapeutic coverage of these structures. How this increased dose delivery may affect a patient’s risk for radiation-related toxicities, however, is currently not well characterized. We hypothesize that near-surface dose to the reconstructed chest wall predicts for an increased risk of significant breast pain as well as the development of acute skin toxicities such as moist desquamation. Identifying dosimetric correlates for these acute toxicities may allow for optimization of radiation treatment planning aimed at reducing the incidence of acute toxicities and further associated complications.
-

Micronutrient deficiencies in Beaumont Integrative Medicine fatigue patients
Jessica Dorschner and Maureen Anderson
Publication Date: 5-2023
Fatigue is a common patient concern at primary care visits and can persist after addressing etiologies such as anemia, infection, malignancy, depression and cardiopulmonary disorders. Micronutrient deficiencies have also been investigated in fatigue patients, particularly individual vitamins such as C, D, B12, E and the mineral zinc. Fewer studies have investigated broad panels of micronutrients in fatigue patients. The Beaumont Integrative Medicine Clinic evaluates many patients with fatigue and assesses micronutrient levels using SpectraCell testing which measures 31 vitamin, mineral and metabolite levels concurrently.
-

Improving Completion Rates of Screening Colonoscopies
Lauren Lumley, Jordan Meyer, and Annie Craib
Publication Date: 5-4-2023
To identify barriers to completion of screening colonoscopies and identify/implement solutions to increase completion rates.
-

Point-of-Care Ultrasound Curriculum Development in a Family Medicine Residency
David Adams, Dylan Rogers, and Jennifer Kowalkowski
Publication Date: 4-28-2022
Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) is an expanding area of medicine and quickly becoming a necessary skill for which clinical physicians must have foundational knowledge1. The goal of our curriculum development is to guide the resident in becoming competent in the use of POCUS to aid in clinical decision making in both inpatient and outpatient settings by providing learning opportunities that will enable residents to develop the knowledge and skills necessary to apply it as a frequently used tool to improve quality and promptness of care.
-

Effects of State-Wide Mandatory Automated Prescribing System on Safe Medication Disposal
Helen E. Huetteman and Elie Mulhem
Publication Date: 5-2-2022
INTRODUCTION
In June 2018, Michigan lawmakers passed new legislation to restrict and monitor controlled substance prescriptions, leading to a significant decrease in the prescribing of opioids. This project aims to evaluate effects of this legislation on safe medication disposal trends throughout the state. -

Documentation of Procedural Training and Competencies in Community-Based Family Medicine Programs
Rohan Venida and Carolyn Nelson
Publication Date: 5-2022
Introduction
Training of common outpatient procedures is an integral and complex part of a Family Medicine residency program. In addition to graduation requirements, many Family Medicine residents strive to become competent in a variety of procedures to maintain a broad scope of practice. It can be a challenge for residency programs to deliver procedural training and have accurate documentation of procedure competency. Training is often predicated on patient volume and patient population exposure, so it can be difficult to adequately train and assess residents in the entire range of procedures. Additionally, programs face challenges such as limited resources, lack of a structured curriculum, limited funds, and lack of time. Smaller programs face even more hurdles, including fewer faculty and limited access to expensive equipment and skills labs. In addition to providing proper training, documentation of competency for various procedures comes with its own challenges, such as the use of paper forms, the costs associated with using a digital app or website for documentation, not having access to the procedure forms on elective or away rotations, the time delay between the preceptor observing the resident’s procedure and documenting feedback, and the inefficiencies of data collection and interpretation. A needs assessment was performed by eleven Family Medicine program directors in Michigan regarding their current methods of procedural training along with challenges they face in training and documenting procedures.
Printing is not supported at the primary Gallery Thumbnail page. Please first navigate to a specific Image before printing.
